
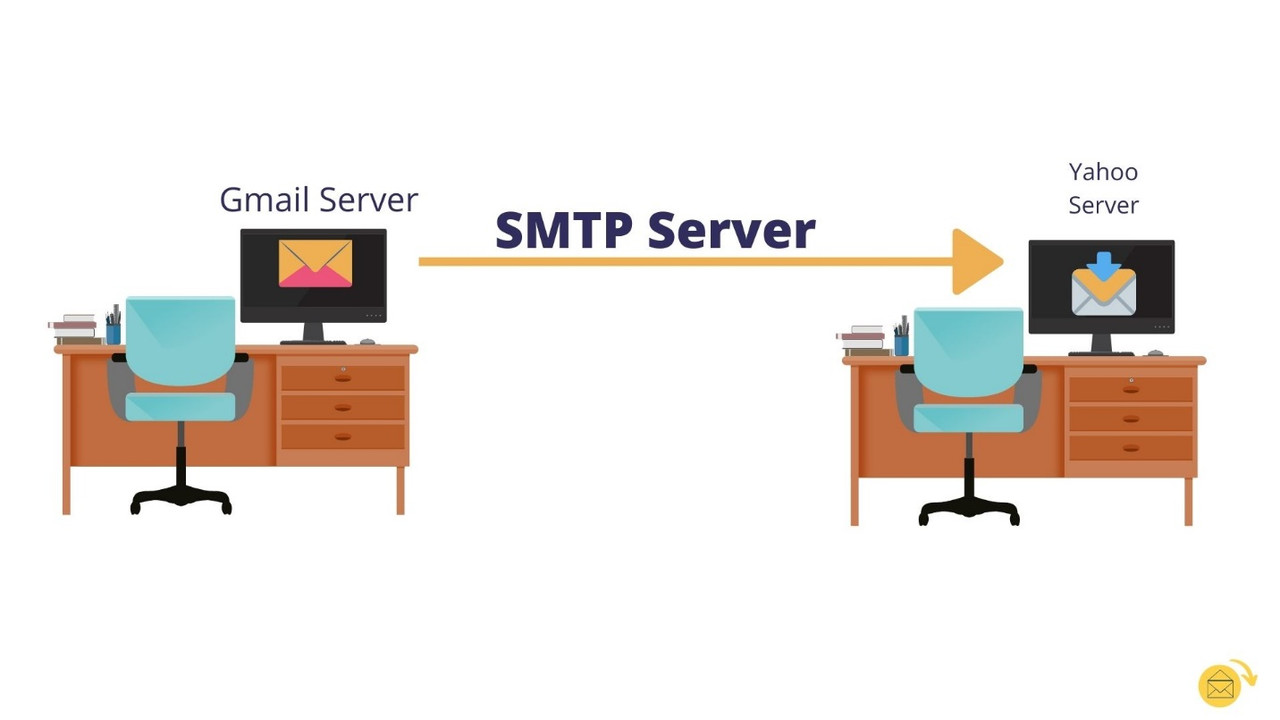
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) servers are specialized computers or software applications responsible for sending, receiving, and routing email messages over the internet. SMTP servers play a central role in the email communication process, ensuring that need more helpLinks to an external site. emails are delivered from the sender's email client to the recipient's email server or email client. Here are key aspects of SMTP servers:
Outgoing Mail Servers: SMTP servers primarily handle outgoing email messages. When you send an email from your email client (e.g., Outlook, Gmail, Thunderbird), the client communicates with an SMTP server to transmit the message to its destination.
Email Transmission: SMTP servers are responsible for initiating the transmission of email messages. They connect to the recipient's email server and transfer the email to the destination server, where it is stored for retrieval by the recipient.
Email Routing: SMTP servers route email messages based on recipient addresses. They use DNS (Domain Name System) to look up the recipient's domain's MX (Mail Exchange) records to determine where to deliver the email.
Authentication: SMTP servers often require authentication to ensure that only authorized users can send emails through the server. Authentication typically involves providing a username and password.
Ports: SMTP servers use specific ports for communication. Port 25 is traditionally used for unencrypted SMTP communication, while port 587 is commonly used for encrypted communication (SMTPS or STARTTLS).
Security: Many SMTP servers support encryption protocols like TLS (Transport Layer Security) or SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) to secure email transmission. This helps protect the confidentiality and integrity of email messages during transit.
Spam Prevention: SMTP servers often incorporate anti-spam measures, such as SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), to verify the authenticity of email senders and reduce spam.
Relaying: SMTP servers can relay email messages, meaning they accept email from email clients and relay them to the recipient's email server. SMTP servers can be configured for specific domains or organizations.
Bounce Handling: SMTP servers handle bounced emails by generating non-delivery reports (NDRs) and notifying the sender when an email cannot be delivered.
Queue Management: SMTP servers manage email queues to ensure the orderly delivery of messages. They retry sending messages that encounter temporary delivery issues.
Authentication and Authorization: SMTP servers may employ various authentication and authorization methods to control who can send emails through the server. This is essential for security and preventing misuse.
Logs and Monitoring: SMTP servers maintain logs and provide monitoring tools for administrators to track email traffic, diagnose issues, and ensure proper functioning.
SMTP servers are a critical component of the email infrastructure, and they work in conjunction with other email protocols like IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) and POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3), which are responsible for receiving and storing email messages on email clients and servers. Together, these protocols enable reliable and efficient email communication.
The best and top SMTP Server Providers
The best SMTP server providers can vary depending on your specific email needs, budget, and preferences. Here are some reputable SMTP server providers known for their reliability and features as of my last knowledge update in September 2021:
SendinBlue: SendinBlue is a popular choice for businesses and marketers. They offer SMTP services as part of their email marketing platform. SendinBlue provides a free plan with daily sending limits and scalable paid plans. Their SMTP services come with email marketing automation and transactional email capabilities.
SendGrid (Twilio SendGrid): SendGrid is a widely recognized SMTP service provider known for its high deliverability rates and developer-friendly features. They offer an email API and SMTP relay services. SendGrid is now part of Twilio and offers a free tier with limited sending.
Mailgun: Mailgun is a transactional email service that offers SMTP relay services. It's popular among developers and businesses for its deliverability features, analytics, and scalability. They provide a flexible pricing model, including a free tier.
Amazon SES (Simple Email Service): Amazon SES is a highly scalable email service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It offers both SMTP and API-based email sending. SES is known for its cost-effectiveness and reliability. AWS provides a free tier with limited sending.
SMTP.com: SMTP.com specializes in transactional and marketing email delivery. They offer both SMTP relay and API-based email sending. SMTP.com is known for its high deliverability rates and sender reputation management.
Postmark: Postmark is a transactional email service focused on deliverability and developer-friendly features. They offer SMTP relay and API options. Postmark is known for its fast email delivery and detailed analytics.
Mailjet: Mailjet is an all-in-one email service provider that offers both SMTP relay and marketing email capabilities. They provide easy-to-use SMTP integration and a user-friendly email marketing platform. Mailjet offers a free plan with limited sending.
Pepipost: Pepipost is an email delivery service with a focus on high deliverability rates. They offer SMTP relay, API integration, and real-time email analytics. Pepipost provides a free plan with daily sending limits.
Elastic Email: Elastic Email offers SMTP services, API integration, and email marketing features. They provide a range of pricing options, including a pay-as-you-go plan. Elastic Email is known for its affordability and scalability.
Mailchimp: While primarily known for its email marketing platform, Mailchimp also offers SMTP services for transactional email. This can be a convenient option if you're already using Mailchimp for marketing campaigns.
When selecting an SMTP server provider, consider factors such as deliverability rates, scalability, pricing, developer-friendliness, and the specific features that meet your email sending needs. Additionally, keep in mind that the email landscape may have evolved since my last update in September 2021, so it's advisable to check the latest reviews, features, and pricing for each provider to make an informed decision.
Top features/config to look for choosing an SMTP Server
When choosing an SMTP server for your email sending needs, it's essential to consider several features and configurations to ensure that it aligns with your requirements and helps Hostuserver you achieve reliable email delivery. Here are some top features and configurations to look for when selecting an SMTP server:
Reliability and Deliverability:
High deliverability rates: Choose an SMTP server with a proven track record of delivering emails to recipients' inboxes rather than spam folders.
Redundancy and failover: Look for redundancy features to ensure email delivery even in case of server failures.
Authentication and Security:
Email authentication protocols: Ensure support for SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) to verify the authenticity of your emails.
Encryption: Choose an SMTP server that supports TLS (Transport Layer Security) or SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) encryption for secure email transmission.
Sending Options:
SMTP relay and API: Consider whether the provider offers both SMTP relay and API-based sending options to accommodate different integration needs.
Custom sender domains: Verify if you can configure custom sender domains to align with your brand.
Scalability:
Scalable sending limits: Ensure that the SMTP server can handle your expected email volume, and check if you can easily scale up or down as needed.
Dedicated IP addresses: For high-volume senders, check if dedicated IP addresses are available to maintain a clean sender reputation.
Email List Management:
Bounce handling: Look for automated bounce handling to manage bounced email addresses and keep your list clean.
Unsubscribe management: Ensure that the SMTP server supports unsubscribe processes to comply with email laws and regulations.
Monitoring and Analytics:
Real-time monitoring: Check if the provider offers real-time monitoring of email delivery, including open rates, click-through rates, and bounce rates.
Detailed analytics: Verify that you can access detailed email performance analytics to measure the success of your email campaigns.
Reliability and Uptime:
Service level agreements (SLAs): Review the provider's SLAs for uptime guarantees and compensation policies in case of downtime.
Support and Documentation:
Customer support: Consider the availability of customer support, including response times and support channels (e.g., chat, email, phone).
Documentation and resources: Ensure that the provider offers comprehensive documentation, guides, and resources to assist with integration and troubleshooting.
Authentication and Authorization:
SMTP authentication: Check if the SMTP server requires authentication for sending emails, enhancing security.
Authorization controls: Look for authorization mechanisms to control who can send emails through the server.
Spam Prevention:
Spam detection and filtering: Verify whether the provider has built-in spam prevention measures to reduce the likelihood of emails being marked as spam.
Feedback loops: Check if feedback loops are available to receive notifications when recipients mark your emails as spam.
Customization:
Custom email headers: Ensure that you can customize email headers and content to meet your specific needs.
Template support: Check if the SMTP server supports email templates for consistent and branded email communication.
Compliance and Legal Considerations:
Compliance assistance: Look for guidance on compliance with email laws and regulations, such as the CAN-SPAM Act and GDPR.
Legal disclaimers: Consider whether you can easily add legal disclaimers and opt-out mechanisms to your emails.
Cost and Pricing Model:
Pricing structure: Understand the provider's pricing model, whether it's based on usage, subscription, or pay-as-you-go.
Cost transparency: Ensure that the provider is transparent about pricing, including any additional fees for specific features or resources.
By carefully evaluating these features and configurations, you can select an SMTP server that meets your email sending needs, enhances email deliverability, and aligns with your organization's goals and requirements.
Approximate price range of SMTP Servers
The cost of SMTP server services can vary widely depending on factors such as the provider, the level of service, the volume of emails sent, and additional features included. Here are some approximate price ranges for SMTP server services based on different use cases and providers as of my last knowledge update in September 2021:
Free SMTP Services:
Some providers offer free SMTP services with limited features and sending limits. These services are suitable for individuals or small businesses with basic email needs.
Price Range: Free to $10 per month for basic plans.
Basic SMTP Services:
Basic SMTP services typically offer higher sending limits and may include features like email authentication and support.
Price Range: $10 to $50 per month for basic plans.
Business SMTP Services:
Business-grade SMTP services cater to small to medium-sized businesses and often include advanced features such as delivery tracking, analytics, and support for larger sending volumes.
Price Range: $50 to $300 per month for business plans.
Enterprise SMTP Services:
Enterprise-grade SMTP services are designed for large organizations and high-volume senders. They offer advanced features, scalability, dedicated IP addresses, and personalized support.
Price Range: $300 to $1,000+ per month for enterprise plans.
Pay-Per-Use SMTP Services:
Some SMTP providers offer pay-per-use pricing, where you are billed based on the number of emails sent. This can be cost-effective for sporadic or variable email sending.
Price Range: Varies based on usage, typically a few cents per thousand emails sent.
SMTP Relay Services:
SMTP relay services, often used for transactional emails, charge based on the number of emails sent. Higher volumes can lead to lower costs per email.
Price Range: Varies based on usage, typically a fraction of a cent per email.
SMTP APIs:
SMTP API services offer programmatic email sending via APIs. Pricing can vary based on API calls or emails sent via the API.
Price Range: Varies based on usage, typically per API call or per email sent via the API.
Additional Costs:
Some SMTP providers may charge additional fees for dedicated IP addresses, dedicated infrastructure, or premium support.
Price Range: Additional costs can vary widely, depending on the specific feature or service.
It's important to note that these price ranges are approximate and may have changed since my last update. Additionally, different providers may offer various pricing models, such as tiered plans, pay-as-you-go, or custom enterprise pricing. When choosing an SMTP server service, consider your email sending volume, required features, and budget to select a plan that meets your needs. Review the pricing details and terms of service of your chosen provider for the most accurate and up-to-date information.
 icons at the top
right corner of the subsection.
icons at the top
right corner of the subsection.